Table of Content
- Is Temu and Shein the same
- Differences between Shein and Temu
- Business Models Differences
- Temu VS Shein Price
- Product Categories and Customer Base Differences
- Temu vs Shein quality
- Temu vs Shein shipping
Is Temu and Shein the same
Temu and Shein are not from the same company; they are two independent companies. Shein entered the cross-border market earlier, starting its overseas business in 2015. Temu, on the other hand, is a subsidiary of Pinduoduo, a famous Chinese e-commerce platform, and began its overseas operations in September 2022, initially targeting the North American market. It later expanded to the UK, Japan, South Korea, and other regions. As of October 2023, Temu has established sites in 40 countries and regions worldwide, covering Europe, North America, Oceania, Latin America, and Asia.
However, the two platforms do share some similarities. Both companies originate from China and are engaged in cross-border e-commerce, expanding into overseas markets. They also have some overlap in the categories they offer, such as clothing and shoes. Therefore, the two platforms are indeed in direct competition with each other. So, what are the differences between them?

Differences between Shein and Temu
Although both are engaged in cross-border e-commerce, there are some differences between Temu and Shein. Let’s take a look at their distinctions in terms of pricing, quality, shipping, business model, product categories and target customer groups.
Business Models Differences
| Platform | Business Models | Further Explanation | Target Suppliers | Pricing Authority |
| Temu | Fully Managed Model | Sellers take in charge of products production and set a factory price; Temu handles everything else, including export, marketing, fulfillment, after-sales service, and final pricing. | Manufacturers in China without local stock or the capability for self-shipping | Temu |
| Semi-Managed Model | Sellers are responsible for listing products, managing inventory, and logistics, while Temu handles advertising, product pricing and sales, and customer service. | Manufacturers in China who have local stock or the capability for self-shipping | Temu | |
| Shein | Semi-Managed Model | Sellers independently select and list products, manage local overseas inventory, and handle fulfillment, while SHEIN provides operational and pricing support | Manufacturers in China who have local stock or the capability for self-shipping | SHEIN and the seller decide through mutual agreement |
SHEIN’s “Semi-Managed” Model
SHEIN has introduced a semi-managed model that allows sellers to independently select and list products, manage local overseas inventory, and handle fulfillment, while SHEIN provides operational and pricing support. This semi-managed model gives merchants more autonomy. Sellers can choose and list products on the platform but must ensure they have local inventory overseas and can fulfill orders locally. Sellers only need to provide the supply price, and SHEIN assists with operations and pricing to facilitate smoother sales. Additionally, this model allows for completely cost-free store setup and sales, with no commissions or monthly fees, making it easier for merchants to manage their stores.
This model does have certain requirements for participating merchants. First, the products must weigh over 400 grams and be stored locally overseas, with the seller responsible for local fulfillment and delivery to consumers. There are no fees to open a store and no performance thresholds required.
Temu’s operational model is divided into fully managed and semi-managed modes.
Temu’s Fully Managed Model
Under Temu’s fully managed model, sellers only need to focus on pricing and manufacturing their products, then send them to Temu’s warehouse in Guangzhou. The platform handles everything else, including export, marketing, fulfillment, after-sales service, and pricing.
This approach alleviates operational burdens for sellers, as they do not need to worry about storage, logistics, or order processing details.
Temu’s Semi-Managed Model
Temu’s semi-managed model offers a flexible, efficient, and cost-effective way for sellers to operate. In this model, sellers can easily set up a semi-managed store as long as they have local stock or the capability for self-shipping/drop shipping.
Sellers are responsible for listing products, managing inventory, and logistics, while the platform handles advertising, product pricing and sales, and customer service.
The key feature of this model is that merchants can leverage overseas warehouses to list and sell products directly on the platform. Temu provides comprehensive support, including advertising, customer service, and sales assistance. Meanwhile, merchants must handle shipping and manage after-sales services like returns and exchanges.
The semi-managed model provides cross-border sellers with a new traffic entry point, allowing them to utilize overseas warehouses and Temu’s platform traffic to sell products with lower costs and less inventory pressure. Additionally, this model helps sellers increase profits and optimize profit margins. By managing their own inventory and logistics, sellers can more effectively reduce costs.
Semi-managed model is particularly suitable for large sellers on Amazon and independent sites, especially those needing to quickly clear inventory, with extensive overseas warehouses and abundant stock across multiple channels.
As e-commerce platforms increasingly demand faster logistics, the importance of local fulfillment capabilities is becoming more pronounced. To achieve local fulfillment, sellers need to leverage self-built warehouses, official warehouses, Amazon warehouses, and third-party overseas warehouses for shipping.
Temu VS Shein Price
It’s not hard to notice that some identical products can have significantly different prices on the two platforms. Generally, products on Temu are priced 30% to even 50% lower than on SHEIN. So, what causes this phenomenon? When discussing prices, we must mention the supply chain, specifically the source factories.
Both Temu and SHEIN source their products from factories in China, and some of these suppliers overlap. This means a supplier might be providing goods to both Temu and SHEIN. Given that the suppliers are the same, why are the prices different?
This brings us to the topic of pricing authority. While both SHEIN and Temu’s semi-managed models target sellers with local overseas stock, their approaches to pricing differ. Temu’s semi-managed model uses platform pricing, while SHEIN’s semi-managed model involves collaborative pricing between the platform and the seller.
Temu follows its parent company’s core strategy, focusing on extreme cost-effectiveness, as reflected in their slogan, “team up, price down.” They adopt a low-margin, high-volume approach, aiming to attract customers and expand the market with low prices. How do they manage to keep prices so low? The main reason is their fully managed model, which saves suppliers from costs associated with warehousing, exporting, marketing, distribution, sales, and after-sales services. Consequently, suppliers lose their pricing power. They only need to report the factory price to Temu, which then decides if the price meets their requirements. If a supplier’s factory price is too high, Temu won’t accept their goods. This creates competition among suppliers—those who offer the lowest factory prices can list their products on the platform. By significantly squeezing supplier profits, Temu can lower product prices to the extreme. Shop and get Temu cash back.
The fully managed model has helped Temu attract a vast number of suppliers. Subsequently, Temu uses a bidding process to select the most cost-effective products and leverages economies of scale to reduce costs associated with operations, advertising, freight forwarding, and last-mile delivery. By extremely compressing the profits of all parties involved, many trading businesses have seen their profits shrink from the multiples they enjoyed in the traditional cross-border e-commerce era to levels comparable to domestic e-commerce’s low-profit margins. This approach achieves the goal of offering the lowest prices in the market.
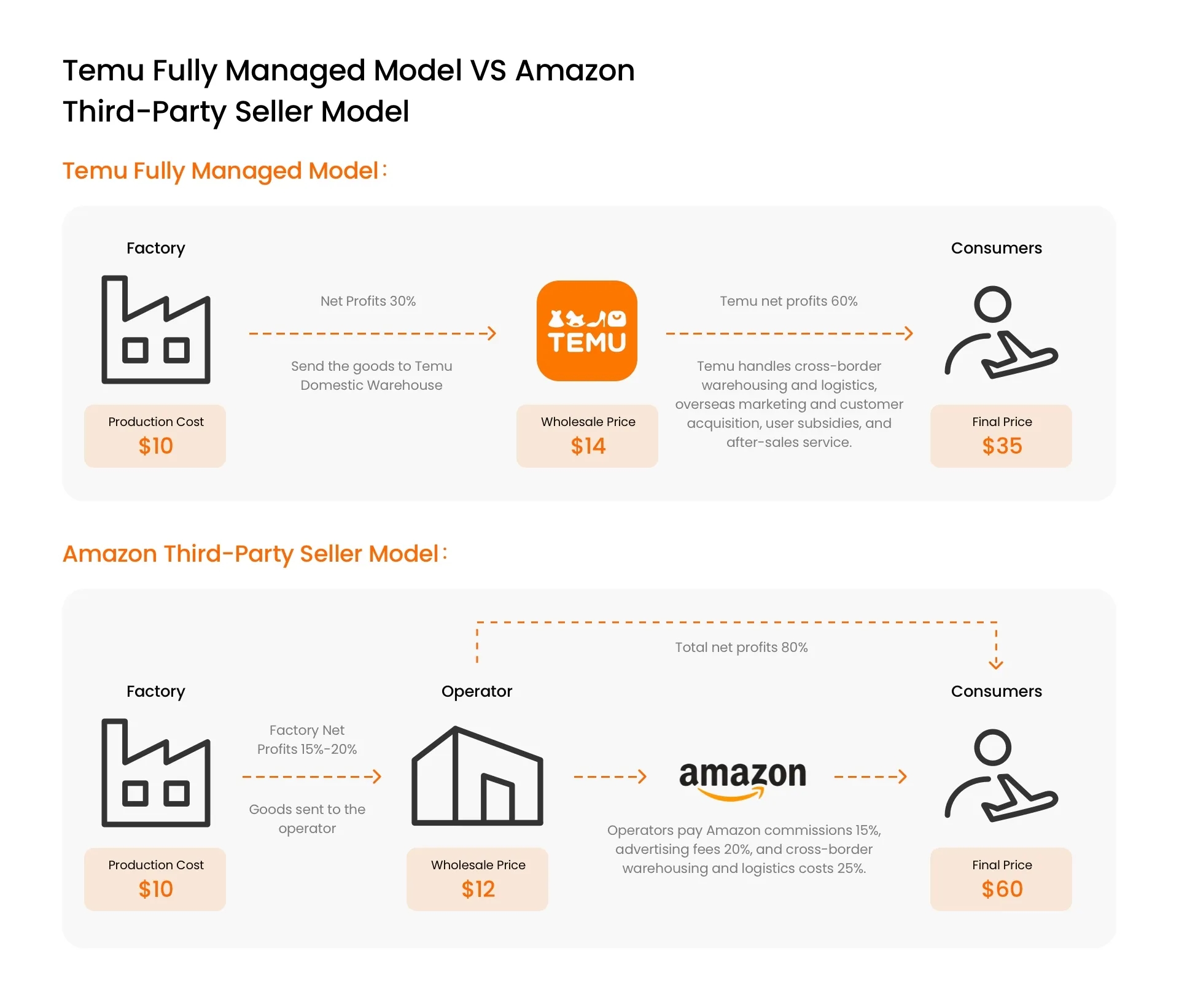
In contrast, SHEIN’s semi-managed model allows sellers to independently select and list products, handle fulfillment, and negotiate prices with suppliers. Therefore, SHEIN’s suppliers typically enjoy higher profits compared to Temu’s suppliers.
Why do suppliers still choose to work with Temu despite the lower profits? The first reason is convenience. Suppliers only need to provide the goods and ship them to Temu’s domestic warehouse, significantly reducing operational costs. For instance, running an Amazon store usually requires more than ten employees, whereas with Temu, only one employee is needed to manage costs, profits, and shipments.
The second reason is that, although the profit margin is small, the order volume is substantial, leading to significant cumulative profits. As we mentioned earlier, Temu focuses on low margins and high volumes. While SHEIN offers higher profits, their order volume doesn’t match Temu’s. This explains why, despite the significant profit squeeze, suppliers still opt to cooperate with Temu.”
Product Categories and Customer Base Differences
Temu is designed as an all-encompassing e-commerce platform, offering a wide range of categories including clothing, beauty, home goods, and pet supplies. On the other hand, SHEIN initially entered the market as a fast fashion platform focused on cross-border e-commerce, primarily dealing in fashion items such as apparel, footwear, and accessories. Over time, SHEIN has also expanded its product categories and platform scope to include beauty products, home goods, and pet supplies. Therefore, as of now, the product categories offered by both platforms are quite similar. The difference lies in the fact that Temu primarily targets low-cost products, while SHEIN places more emphasis on fashion and brand appeal.
Temu operates on a group buying model, where users can enjoy lower prices by inviting friends and participating in group purchases. This approach fosters interaction and sharing among users and appeals to those who enjoy group buying and are looking for bargains. In contrast, SHEIN is a cross-border e-commerce platform focused on individual shopping, emphasizing personalization and quality. SHEIN’s primary users are young women who seek fashion and style, paying close attention to the design and aesthetics of the products.
In terms of customer base, SHEIN tends to attract a younger demographic, whereas Temu has a larger proportion of slightly older customers.


Image:businessoffashion.com
Temu vs Shein quality
The quality of products largely depends on the suppliers. As mentioned earlier, Temu and SHEIN might share some of the same suppliers, leading to situations where identical products have different prices on the two platforms.
However, overall data indicates that the return rate for clothing on Temu is generally higher than on SHEIN. This is because SHEIN started as a fast fashion clothing retailer and has accumulated a mature supply chain both domestically and internationally over time. SHEIN offers a large number of its own branded products. Under this brand model, SHEIN manages the entire process from product design, line planning, fabric procurement, production, sales, to marketing. Partner factories supply goods according to SHEIN’s standards and requirements, which helps maintain better control over product quality.
On the other hand, Temu focuses on extremely low prices, which may result in less stringent quality control compared to SHEIN. Nevertheless, Temu’s products mainly come from suppliers on its parent company Pinduoduo’s platform. These suppliers have already been vetted and screened by Pinduoduo, which ensures a certain level of quality and reliability.
Temu vs Shein shipping
Shipping cost
For standard shipping, Temu offers free delivery for most orders. However, if you need expedited shipping, Temu charges an additional fee.
Similarly, SHEIN provides free standard shipping, but this is subject to a minimum order amount, typically over $49. For expedited shipping, SHEIN also charges an extra fee.
Shipping time
SHEIN’s delivery time depends on the items you purchase and the order amount. Since SHEIN has some warehouses in Singapore and the United States, if the item is already in a warehouse located in the buyer’s region, the delivery time will generally be faster. You can check the estimated delivery time on the order page when you make your purchase.
Temu operates on a fully managed model and does not yet have overseas warehouses. All shipments originate from China, so the delivery time is typically longer. The specific delivery time can also be found on the order page when you place your order.
| Platform | Shipping Method | Shipping Time | Shipping Costs |
| Temu | Standard Shipping | 6 – 22 days | FREE on all orders |
| Express Shipping | 4 – 11 days | $12.90 – orders < $129.00 Free – orders ≥ $129.00 | |
| Shein | Standard Shipping | 10-15 days | $3.99 Free – orders over $29.00 |
| Express Shipping | 7-11 days | $12.90 Free – orders over $129.00 |

